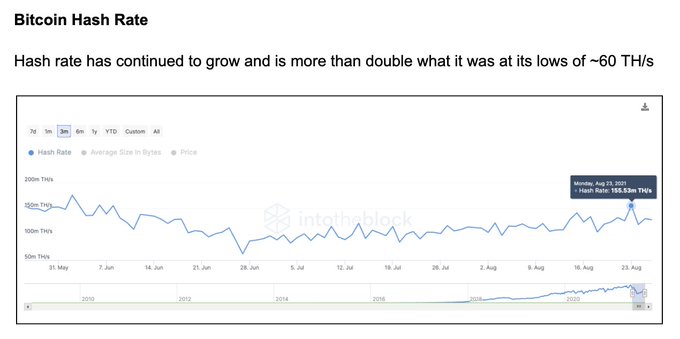
Bitcoin’s hashrate has been on the right footing because it has more than doubled, as disclosed by research analyst Nick Mancini.

In July, the hashrate plummeted by 50% amid intensified crypto mining crackdowns by Chinese authorities.
The hashrate is used to measure the processing power of the BTC network. It allows computers to process and solve problems that enable transactions to be approved and confirmed across the network.
In June, Chinese authorities disconnected BTC mining sites in Sichuan. As a result, more than 90% of China’s crypto mining capacity was hampered. As a result, this clampdown left miners with no choice but to shut down operations and move elsewhere.
Nevertheless, the upward trajectory in BTC’s hashrate has been caused by a shift from the East to the West, with the United States being the largest beneficiary.
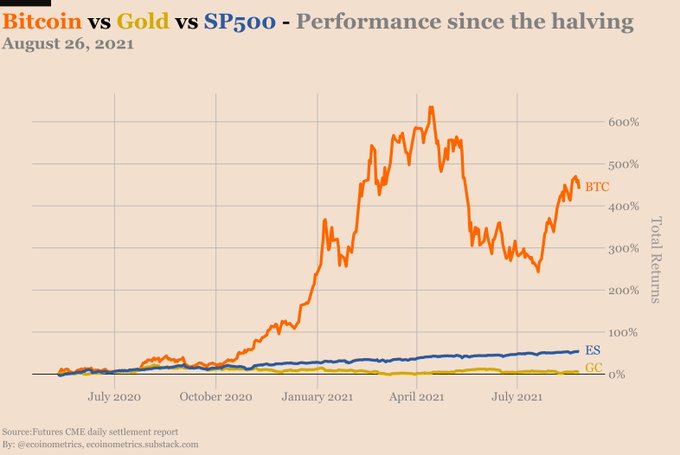
Bitcoin records exemplary performance since the halving
According to on-chain data provider Ecoinometrics, Bitcoin has been up by more than 441% since the halving event of last year. Consequently, the S&P Index and gold have increased by at least 53.1% and 5.53%, respectively, under the same period.
Bitcoin halving refers to the reduction of Bitcoin block rewards, which occurs once every 210,000 blocks are created, and it usually happens around every four years. Block reward refers to the amount of Bitcoin received by miners after they successfully validate a new block. The rationale behind this is Bitcoin’s design, whose total supply is capped at 21 million coins.
Bitcoin’s third halving took place on May 11, 2020, effectively reducing the block rewards from 12.5 to 6.25 BTC per new block. The decay was the third time in its history that this event happened, as the previous ones occurred in 2012 and 2016. Precisely, Bitcoin’s block rewards went down to 25 from 50 Bitcoin per block in November 2012. It further decreased to 12.5 units in July 2016.
The logic behind halving events is that more BTC gets mined as more people utilize the Bitcoin network. Therefore, by slashing the mining rewards by half, retrieving this digital asset becomes difficult, increasing its value based on limited supply.
Image source: Shutterstock